Receive Honest News Today
Join over 4 million Americans who start their day with 1440 – your daily digest for unbiased, fact-centric news. From politics to sports, we cover it all by analyzing over 100 sources. Our concise, 5-minute read lands in your inbox each morning at no cost. Experience news without the noise; let 1440 help you make up your own mind. Sign up now and invite your friends and family to be part of the informed.
Good morning! Today is Friday, May 16, 2025.
We have some exciting AI news today: Windsurf has launched its own AI models tailored for software engineering, and Walmart is gearing up to accommodate AI shopping agents.
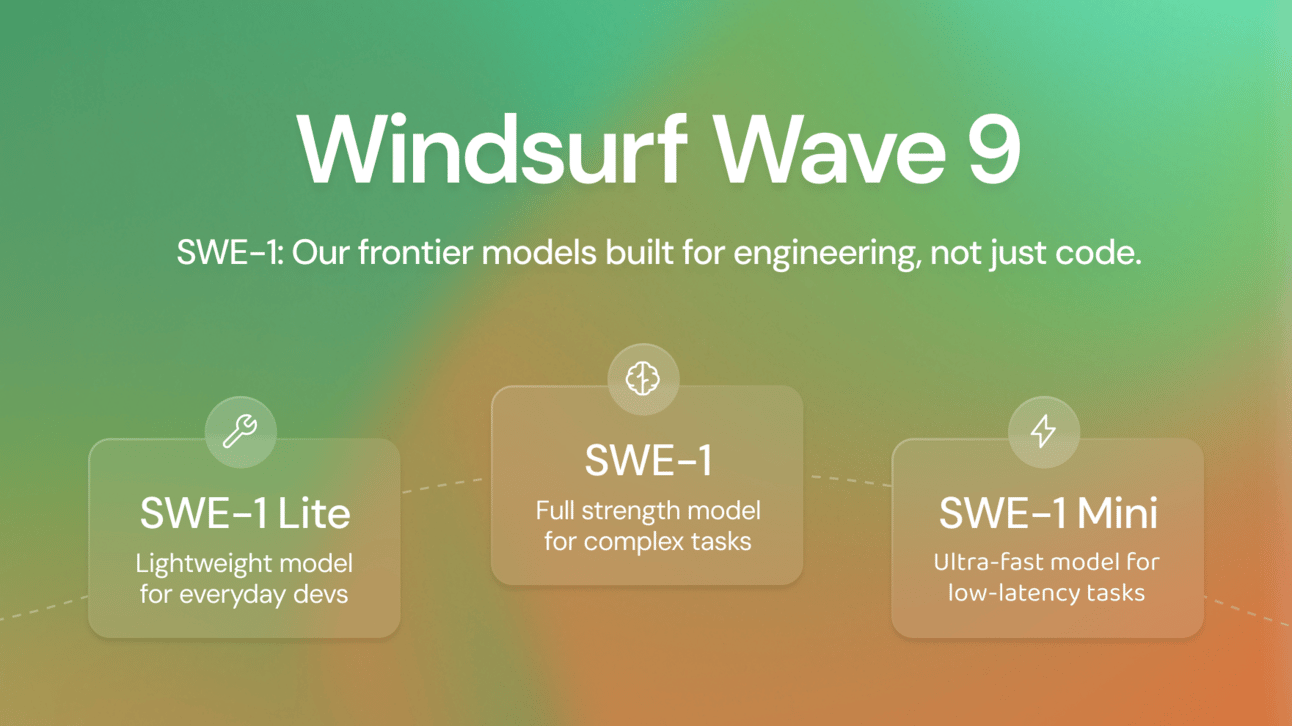
1. Windsurf Launches In-House AI Coding Models Ahead of OpenAI Acquisition
Vibe-coding startup Windsurf has unveiled its first family of AI models: SWE-1, SWE-1-lite, and SWE-1-mini, designed to support the full software engineering process, not just code generation. The move signals Windsurf’s shift from relying on external AI providers to building its own models, even as OpenAI reportedly finalizes a $3B deal to acquire the company. SWE-1 competes with top models like GPT-4.1 and Claude 3.5 Sonnet on internal benchmarks and aims to handle complex workflows across terminals, IDEs, and more.

2. Walmart Prepares for the Rise of AI Shopping Agents
Walmart is gearing up for a future where your next shopper might be an AI bot, not a person. As autonomous shopping agents like OpenAI’s Operator begin handling tasks like restocking groceries or buying TVs, Walmart is adapting its product listings, pricing strategies, and digital infrastructure to appeal to both humans and bots. The retail giant is also developing its own AI agents within its app to assist customers directly, while anticipating a future where third-party bots dominate. It’s a fundamental shift that could reshape how advertising, search, and online shopping work.

3. Google Rolls Out AI Accessibility Upgrades for Android and Chrome
In celebration of Global Accessibility Awareness Day, Google has launched a suite of new AI-powered accessibility features across Android and Chrome. Highlights include Gemini integration with TalkBack, allowing users with vision impairments to ask questions about on-screen images, and a new “Expressive Captions” feature that captures not just what’s said, but how it’s said, like stretching out “nooo” or emphasizing an “amaaazing” sports play. Google is also expanding support for speech recognition in African languages and making scanned PDFs readable in Chrome with new OCR tech.

4. Google One Surges to 150M Subscribers, Thanks to AI Perks
Google’s subscription service, Google One, has hit 150 million users. A 50% jump since early 2024, fueled by demand for its new AI-powered features. Launched in February, the $19.99/month tier offers exclusive AI tools, drawing in millions of subscribers and signaling a shift in how Google monetizes AI beyond ads. As traditional search faces disruption from AI chatbots, Google is betting big on subscriptions to diversify revenue and future-proof its business.

5. Meta Hits Pause on “Behemoth” AI Model Over Concerns It’s Not a Big Enough Leap
Meta has delayed the release of its much-anticipated “Behemoth” AI model, its largest version of Llama 4, amid worries it may not offer a significant improvement over previous models, according to a new Wall Street Journal report. Originally planned for release this spring, the model is now expected in the fall at the earliest. The setback reflects a broader industry trend: making AI models simply "bigger" may no longer be delivering the breakthroughs it once did.

6. AI Breakthrough Can Predict Where Any Protein Lives in a Human Cell
MIT, Harvard, and Broad Institute researchers have developed an AI model called PUPS that can predict the location of virtually any protein within any human cell, no lab required. Trained on protein sequences and cell images, the system combines language and vision models to pinpoint where proteins live in individual cells, even ones it has never seen before. This leap could accelerate drug discovery, disease diagnosis, and understanding of complex biological processes, cutting months of lab work down to seconds of computation.
How would you rate today's newsletter?
Stay tuned for more updates, and have a fantastic day!
Cheers,
Zephyr